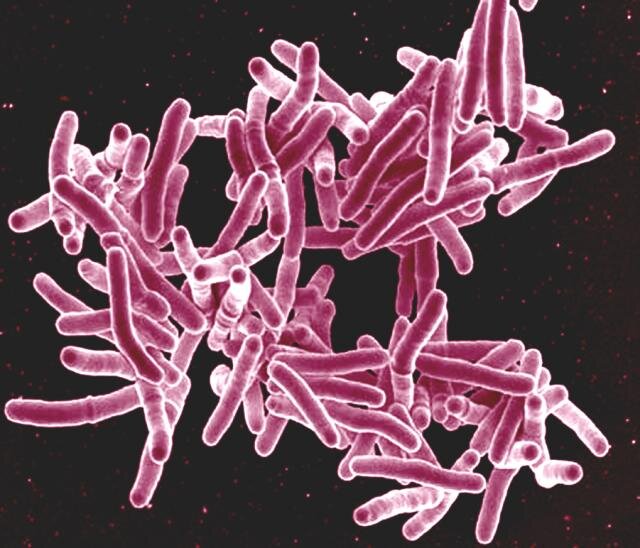
Rutgers Health research has uncovered why a relatively new antibiotic for tuberculosis (TB) works against multidrug-resistant strains, potentially inspiring improved treatments and drug development strategies.
The study by scientists at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School and other institutions found that deficiencies in a critical enzyme make tuberculosis bacteria that resist old antibiotics more vulnerable to the new antibiotic bedaquiline.
Study Paper:
Catalase activity deficiency sensitizes multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis to the ATP synthase inhibitor bedaquiline
You must log in or # to comment.